Database Development: The Backbone of Modern Digital Systems
In the architecture of a modern software application from simple mobile apps to the most complex SaaS platform, the database serves as an absolute foundation. It is responsible for secure, reliable, and high-performance storage, retrieval, and management of business-critical data.
Poorly designed databases lead to slow performance, increased downtime, data loss, security risks, and scalability nightmares.
A well-engineered database, on the other hand, delivers speed, integrity, automation, and long-term cost efficiency.
What is Database Development?
- Designing how data will be stored
- Data relationship structuring
- Implementing and optimizing the database engine
- Ensuring performance, security, and scalability over time
📌 It is not just “creating tables” — it is the brain of an application.
The Database Development Lifecycle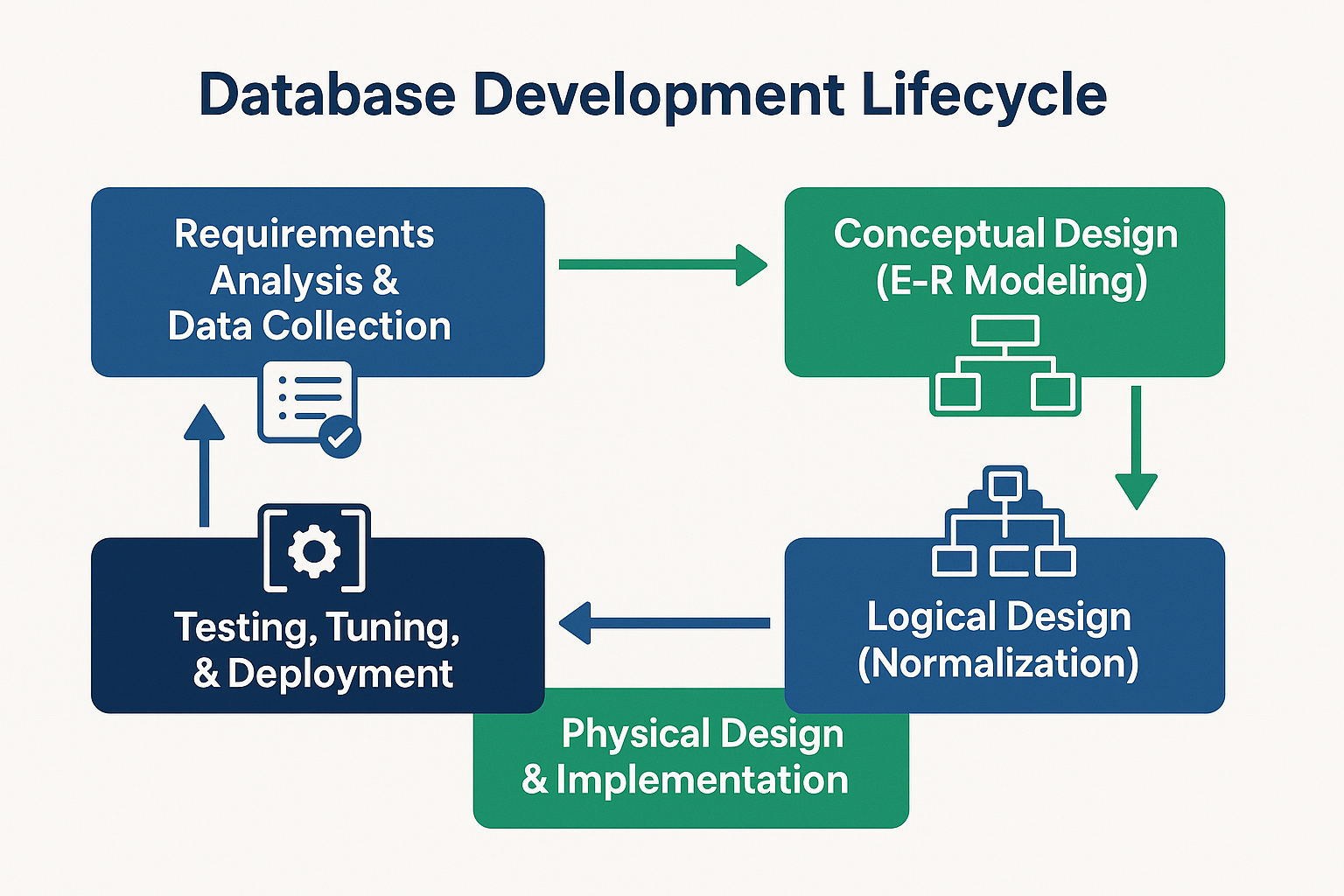
- Requirements Analysis & Data Collection
- Conceptual Design (E-R Modeling)
- Logical Design (Normalization)
- Physical Design & Implementation
- Performance Testing, Optimization & Deployment
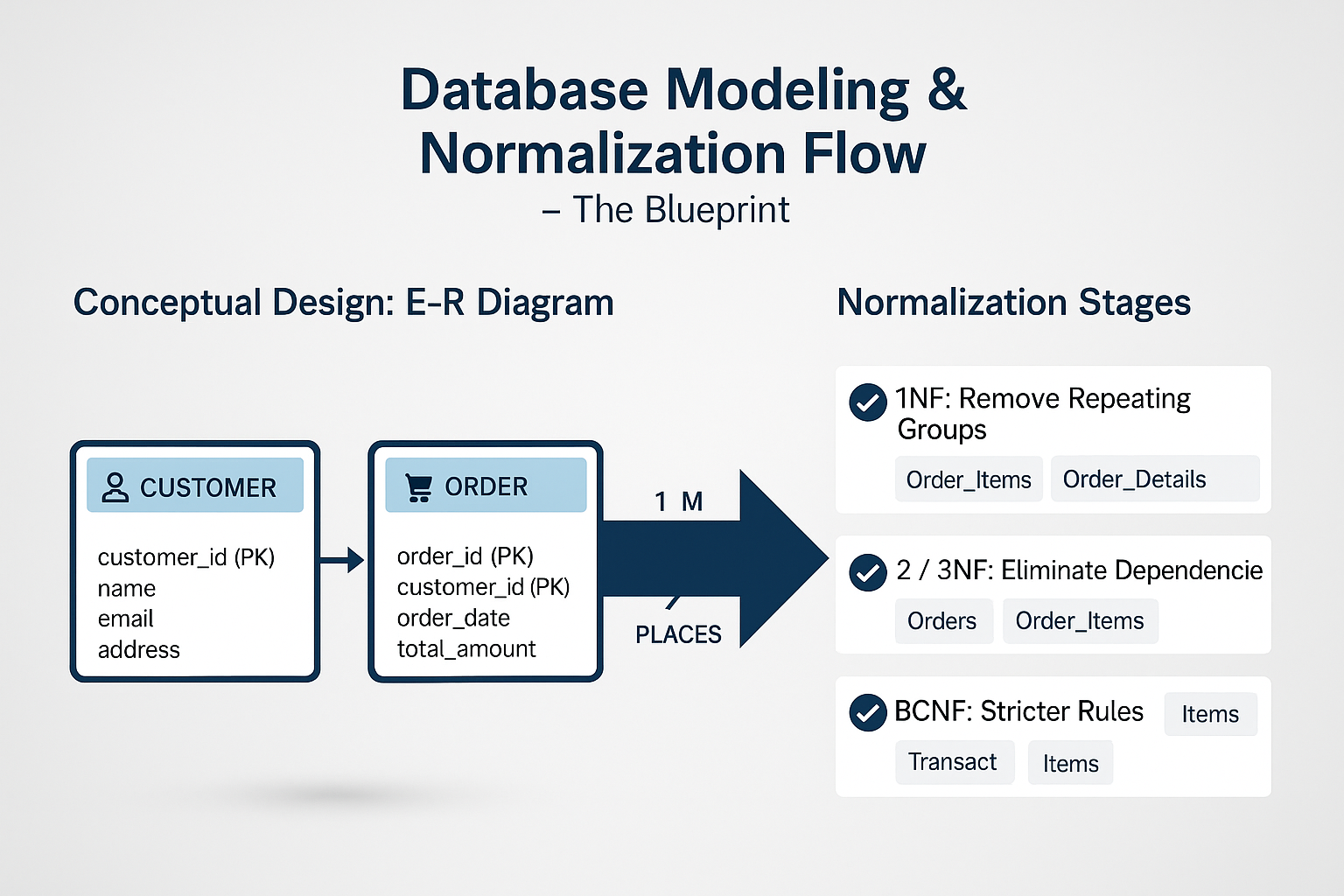
Data Modeling & Design — The Blueprint
Data modeling converts business rules into database structure. Most important tool: Entity-Relationship (E-R) Diagram.
- Shows entities (Customer, Order, Product…)
- Shows attributes (Name, Price, Email…)
- Shows relationships (One-to-Many, Many-to-Many)
Note: If E-R modeling is wrong → the entire system becomes unstable.
🔹 Normalization (for Relational Databases)
Normalization removes redundancy and ensures clean, maintainable data.
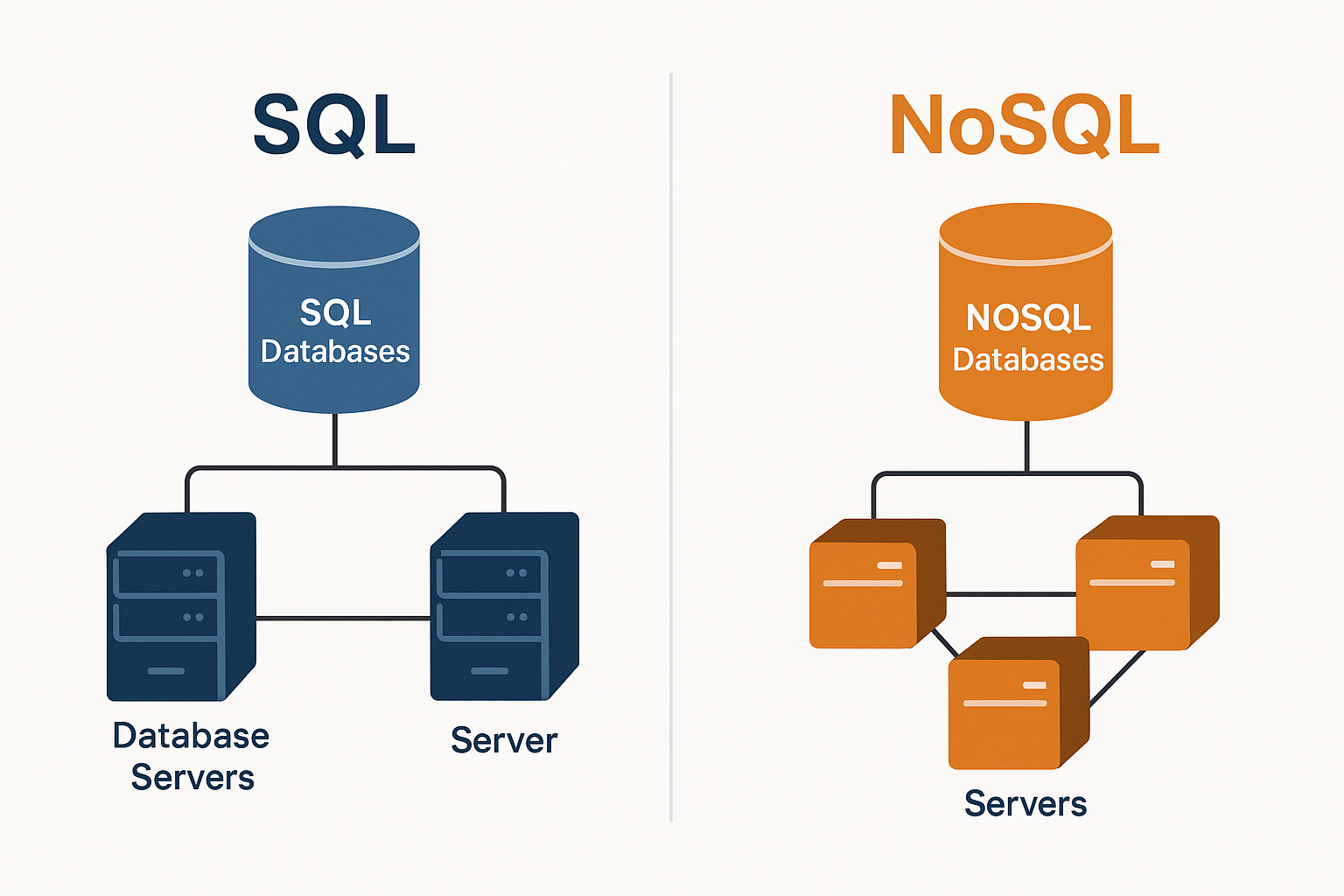
⚙️ Choosing the Right Database Technology
Technology always depends on traffic, scalability, cost and data structure needs.
🔹 Popular SQL Databases
🔹 Popular NoSQL Databases
🚀 Optimization & Performance Tuning
This is the phase that transforms a database from a basic working system into a high-performance, enterprise-grade engine capable of handling massive workloads with consistency and speed.
🔑 Key Optimization Methods
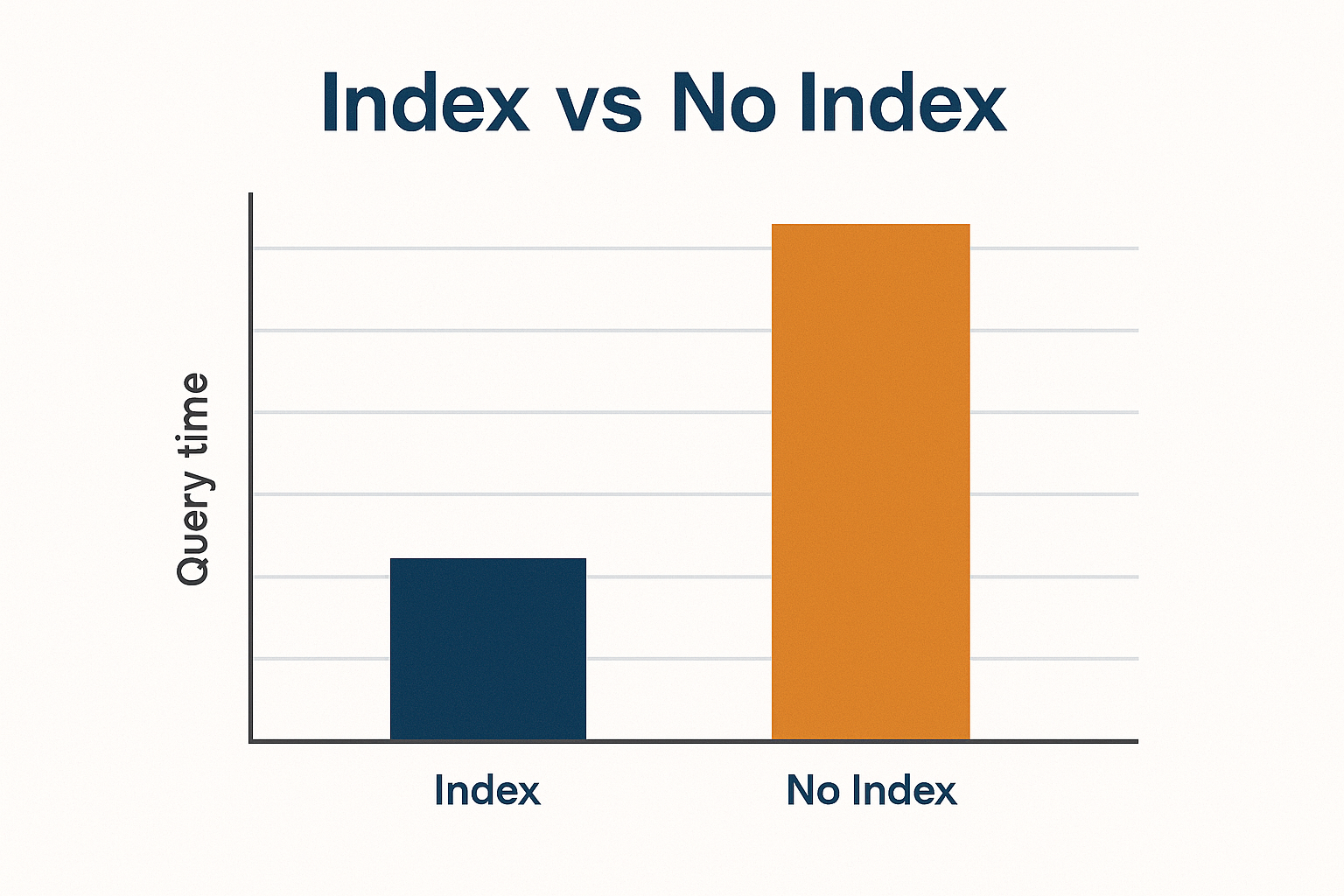
- Indexing → Speeds up search operations
- Query Optimization → EXPLAIN, reduce disk I/O
- Caching → Redis / Memcached to reduce DB load
- Denormalization → Faster reads for analytics systems
🔐 Security & Compliance (Non-Negotiable)
Modern data laws demand strict protection.
- Encryption (in transit & at rest)
- Least Privilege Access (PoLP)
- Parameterized Queries (SQL Injection prevention)
- Data Masking / Tokenization
- Regular Monitoring & Audits

Conclusion — Database Development is a Competitive Advantage
A professionally developed database is not an expense — 💡 It is a long-term asset that drives scalability, stability, and business growth.
It delivers:
- Faster systems & happier users
- Smarter data analytics & automation
- Lower infrastructure cost over time
- Ability to scale to millions of users without breakdown
🔥 A well-engineered database is the power engine behind every successful digital product.