What Is Information Management? Meaning, Importance & Real Examples Explained
What is Information Management?
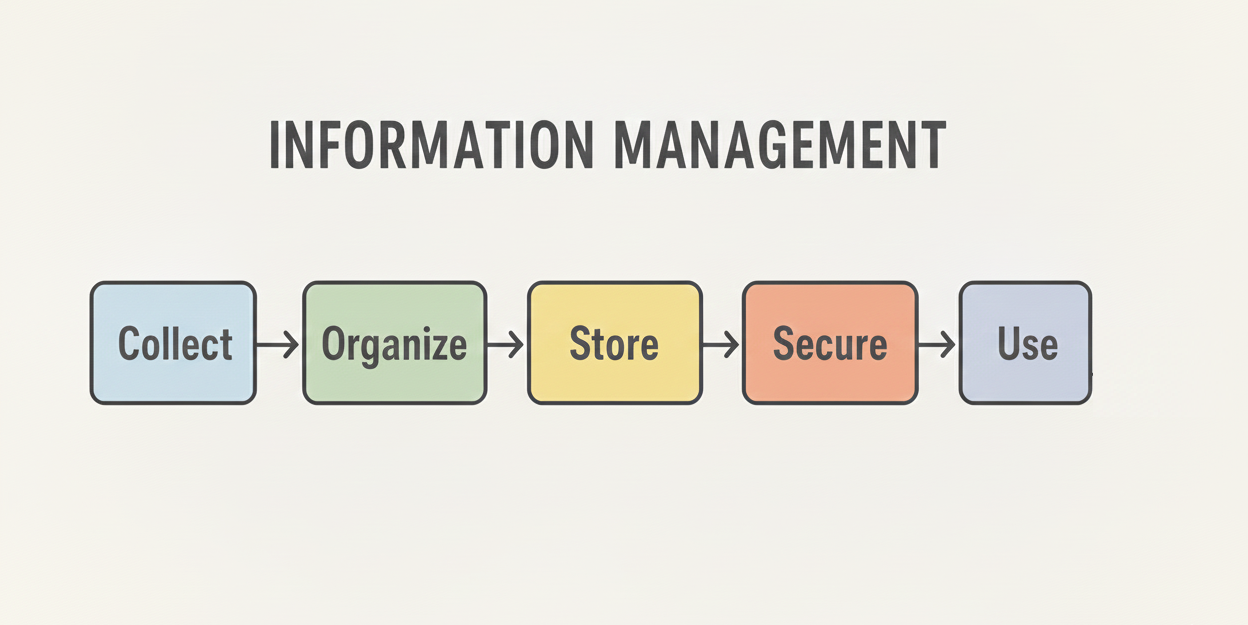
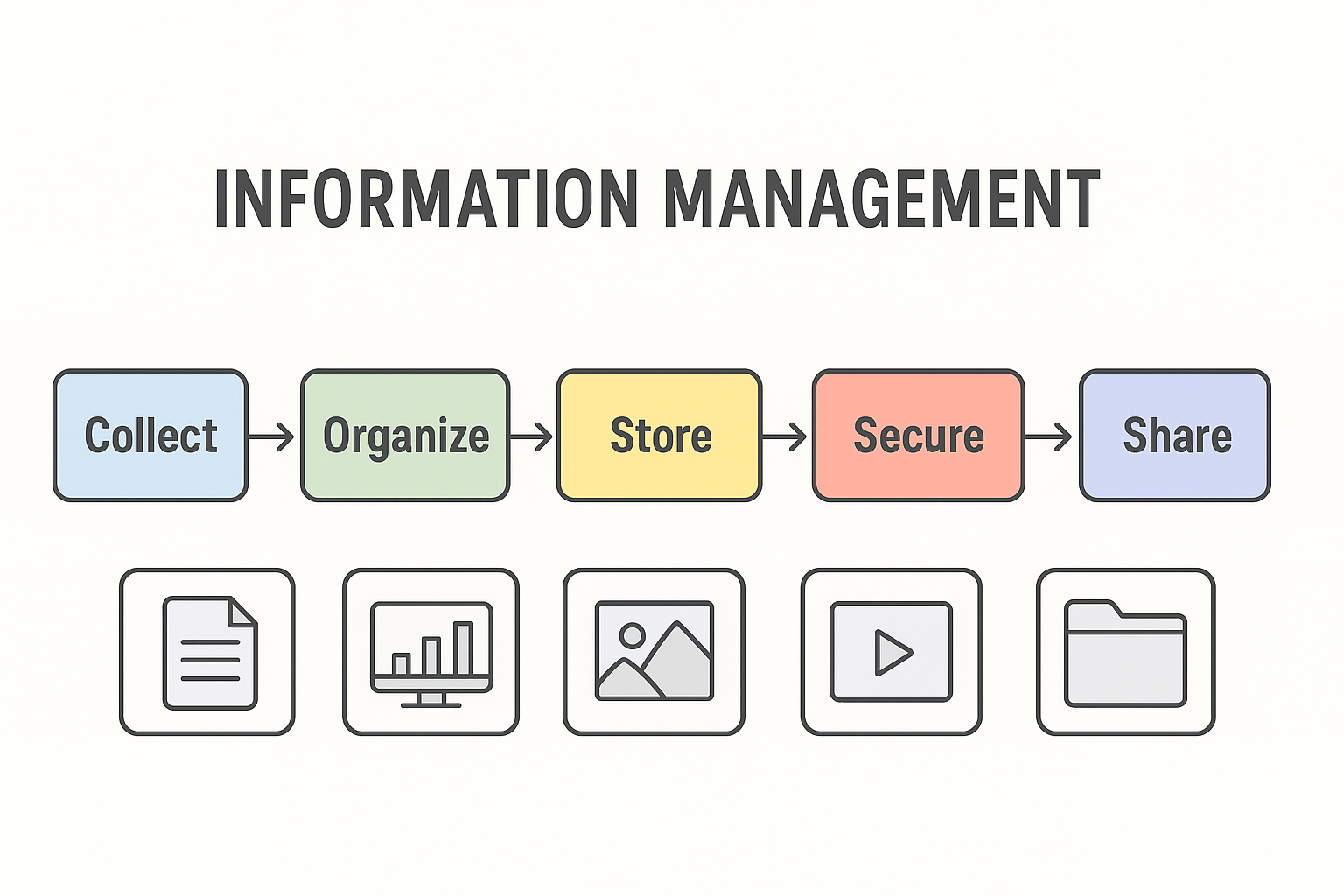
Information Management (IM) means collecting, organizing, storing, securing and using information in the right way.
In today’s digital world, information exists everywhere—emails, documents, apps, websites, photos, videos and databases.
IM ensures that this information stays organized, accurate, safe and easily accessible whenever we need.
Why is Information Management Important?
Good information management helps individuals and businesses work smarter and faster.
Here are the major benefits:
- 1. Faster Decision Making: Right information at the right time helps to take better decisions.
- 2. Saves Time: Well-organized data reduces confusion and makes the work efficient.
- 3. Increased Productivity: Employees spend less time on searching and spend more time in working.
- 4. Better Data Security: Protects sensitive information from leaks, misuse or loss.
- 5. Reduced Costs: Reduce duplication and unnecessary storage expenses.
- 6. Legal Compliance: Helps companies follow data privacy rules and regulations.

How Information Management Works (Step-by-Step)
Here is the simplified process:
- 1. Information Collection:
Data comes from:
- Emails, Forms, Surveys, Documents
- Customer interactions, Apps & websites
- 2. Organizing Information:
This includes:
- Folder structures, Tags, Categories, Naming standards, Metadata
- 3. Storing Information:
Data can be stored in:
- Cloud storage (Google Drive, OneDrive), Company servers, Databases, Document management systems
- 4. Securing Information:
Security includes:
- Password protection, Encryption, Access control, Backup & recovery systems
- 5. Sharing & Using Information:
Authorized teams or individuals use the information to work, collaborate and make decisions.
- 6. Archiving or Deleting Information:
Old or unnecessary data is archived for future reference or securely deleted.

Types of Information Management
- 1. Data Management: Managing numbers, analytics, statistics and structured datasets.
- 2. Document Management: Managing PDFs, Word files, spreadsheets and text files.
- 3. Knowledge Management: Managing experience-based information like guides, best practices, training content.
- 4. Records Management: Managing legal documents, contracts, policies, invoices, and compliance records.
- 5. Digital Asset Management: Managing media files like images, logos, videos, brand assets, audio files.
What is an Information Management System (IMS)?
An Information Management System is a software platform that helps store, organize, secure and manage information.
Popular IM Systems
- Microsoft SharePoint
- Google Workspace
- Notion
- Airtable
- Zoho Docs
- ERP systems
What an IMS Does
- Stores all information in one place
- Ensures fast searching
- Helps teams collaborate
- Improves data security
- Automates workflows

Best Practices for Effective Information Management
To manage information properly, follow these proven practices:
- ✔ Use clear and short file names
- ✔ Maintain a consistent folder structure
- ✔ Regularly back up data
- ✔ Set access permissions
- ✔ Avoid duplicate files
- ✔ Remove or archive old data
- ✔ Create an information management policy for your team
Real-Life Examples of Information Management
- 1. Hospitals: Patient records, medical history, and reports are stored digitally for quick access.
- 2. E-commerce Companies: Order data, customer data, and payment records are organized in secure systems.
- 3. Schools & Colleges: Student data, attendance, results, and fee details are managed in school management systems.
- 4. Corporate Offices: Documents, HR files, client data, and project records are stored in cloud systems like SharePoint.
Future of Information Management (2025 and Beyond)
The future of IM is AI-driven, automated, and more intelligent.
Upcoming Trends
- AI auto-tagging files
- Smart search using natural language
- Predictive analytics
- Automated backups
- Voice-based information access
- Advanced cybersecurity

Conclusion
Information Management is essential for every business, student, and professional.
It improves productivity, saves time, increases security and helps to make smarter decisions.
In a world where data grows every second, good information management is not a choice — it’s a necessity.